AI-Powered Energy Optimization. Unlock Cost Savings.
From hourly energy analytics to thousands of AI-driven retrofit simulations, NZero empowers organizations to optimize their energy usage with precision and speed.







From hourly energy analytics to thousands of AI-driven retrofit simulations, NZero empowers organizations to optimize their energy usage with precision and speed.
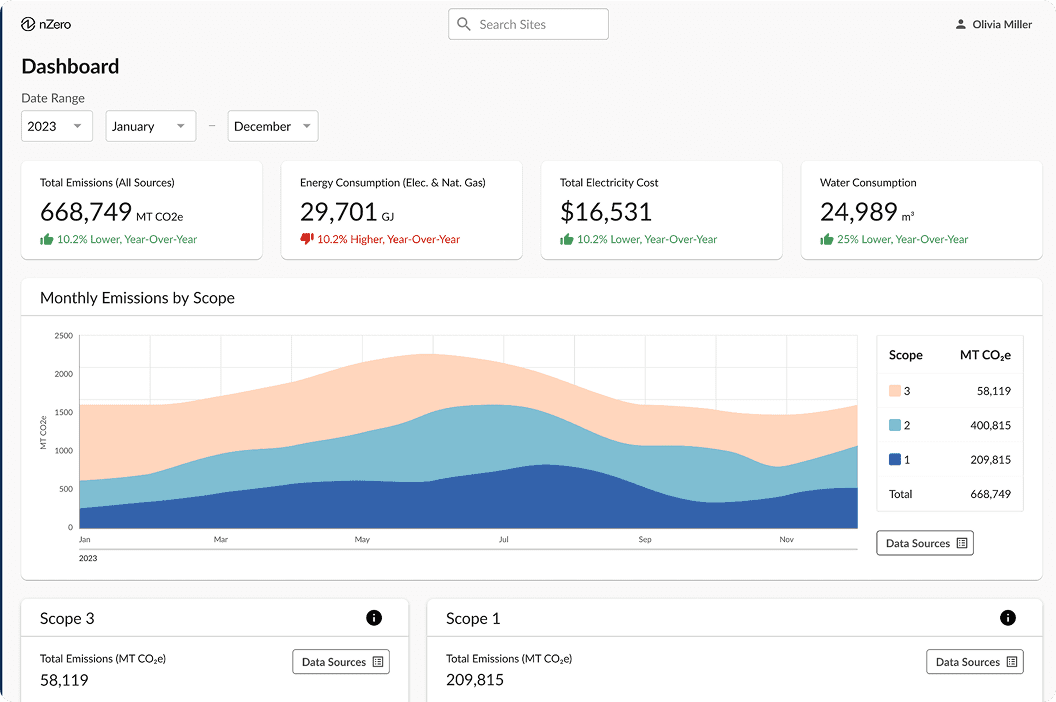
Achieve higher precision in your energy data compared to any other platform.
Save significantly on the expenses related to manual, on-site energy audits.
Replace manual reporting processes with seamless, automated efficiency


From automated data collection to AI-powered retrofit planning, NZero provides the tools you need to turn sustainability goals into reality.
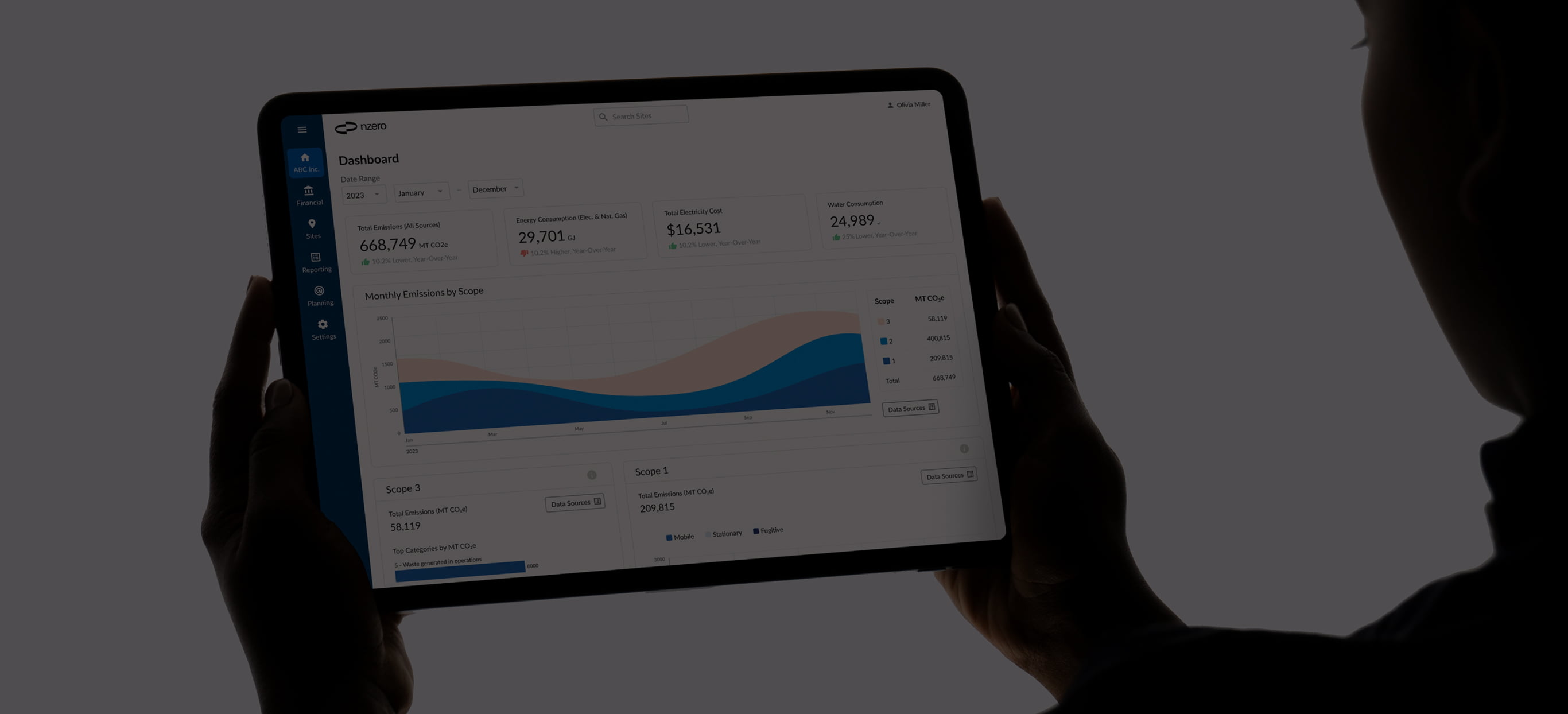
Eliminate manual entry and get audit-ready electricity, water, natural gas, and steam data with automated ingestion and AI-powered data completion.
Target and reduce costly peak demand through peak shaving and load shifting using hourly data visualization, pattern recognition, and real-time verification.
Simulate thousands of energy retrofit scenarios to identify the optimal mix for your budget, efficiency improvements, and carbon reduction goals.
Connect to utility providers and pull bills automatically—without your team lifting a finger.
Fill missing data via AI using time-of-day, weather, and weekday patterns to generate realistic, highly accurate estimates.
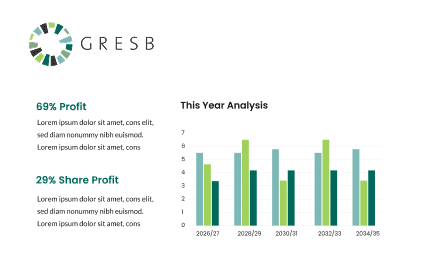
Easily export reports aligned with global standards like GRESB and GRI.


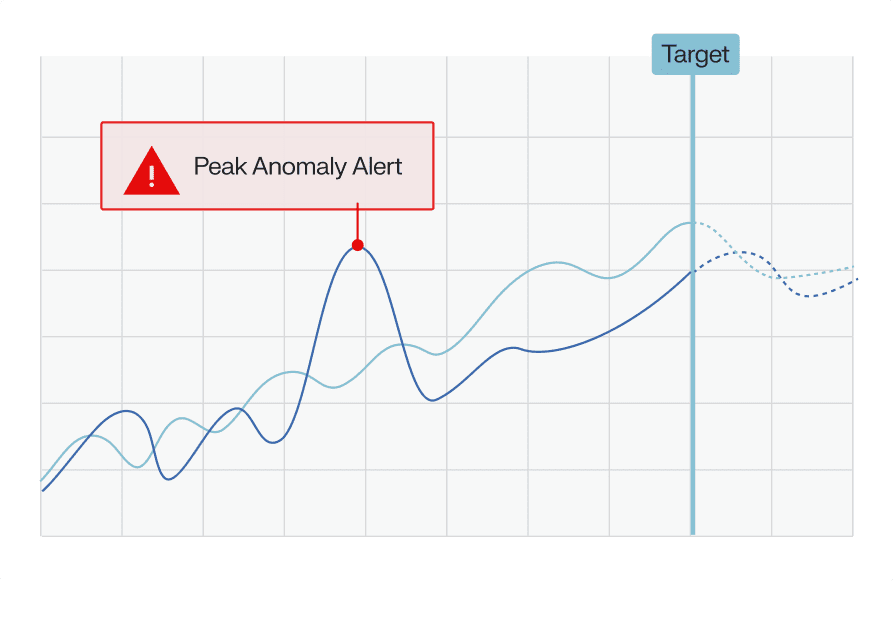
AI continuously analyzes usage to identify peak load trends and site-level anomalies as they happen.
Verify that every peak reduction measure results in a measurable demand drop, confirming your strategy's effectiveness.
Ask "Which site had the biggest overnight spike?" and get clear, data-backed answers to guide action.



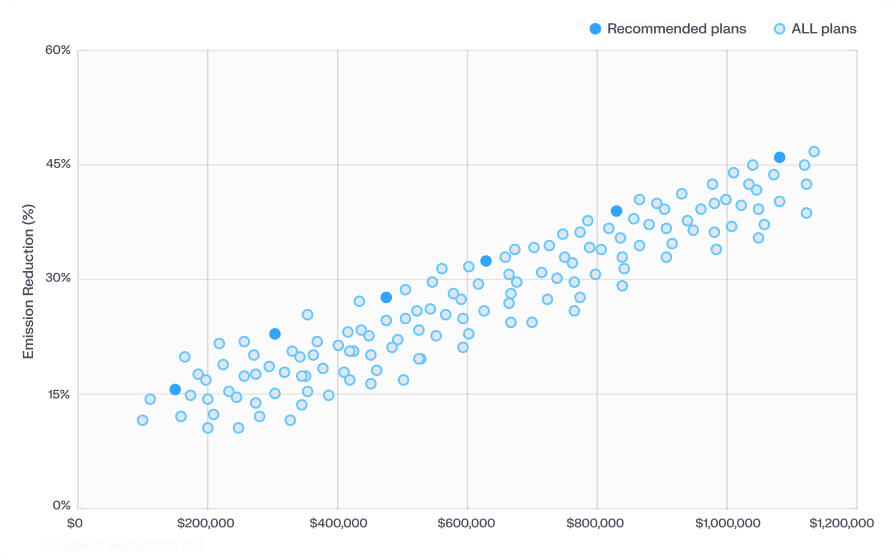
Model solar + insulation + HVAC upgrades together to get realistic projections based on your specific site conditions.
Each scenario is scored by ROI, annual savings, and emissions reduction to prioritize based on cost and climate goals.
Our AI ranks which sites should be upgraded first, so you invest where it matters most.


NZero is built to serve the unique needs of leaders across the public and private sectors.
See how leaders are using NZero to achieve their decarbonization and financial goals.


Whether you're managing your own portfolio or advising others, NZero has a solution built for you.

Built for scale and designed for partners, OS is the customizable platform for delivering elite sustainability counsel and helping clients move from plan to action.
Awards & Certifications
2023
Business Intelligence
Group
Small Business of the Year
2022
Business Intelligence
Sustainability Product of the Year
2022
Time Magazine
Best Inventions
2022
Fast Company
World-Changing Ideas
2022
AICPA | SOC

How ASUENE’s mergers and acquisitions are accelerating the green transition in U.S. business

ASUENE Enters U.S. Climate Tech Market with Acquisition of Carbon Accounting Startup NZero

Washoe County and NZero Bring Data Transparency to Climate Action

Data Center Growth Is Forcing a Rethink of Energy Management

Global Energy Transition Investment Reaches $2.3 Trillion in 2025 as Corporate Decarbonization Pressure Intensifies

FERC: US Peak Electricity Demand Is Rising 24 Percent Above Previous Forecasts

Stop guessing and start making data-driven decisions. See how NZero can transform your energy management and decarbonization strategy.
Request Your Personalized Demo