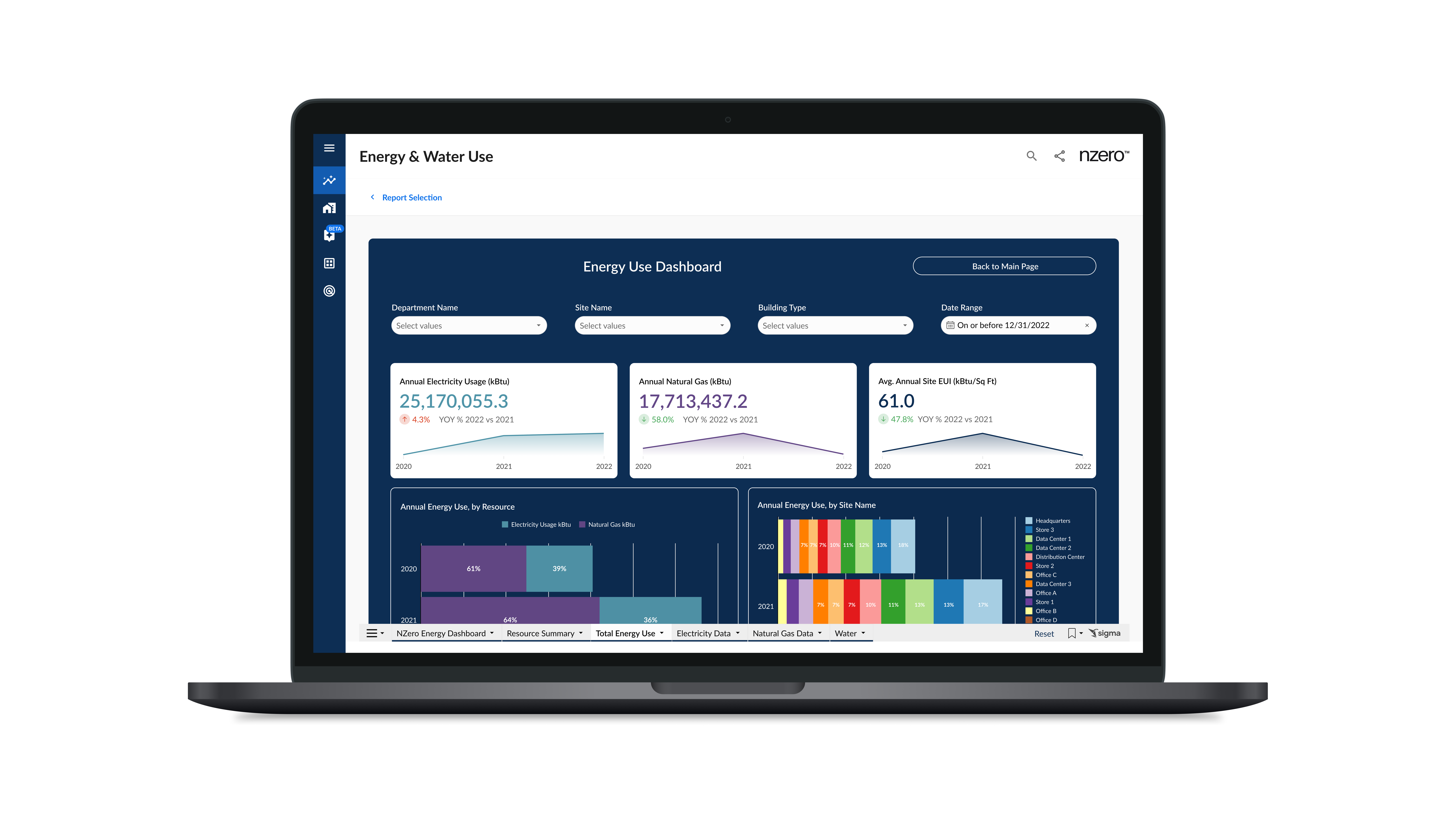
The Value of Hourly Data and Integrated Insights
Monthly utility bills don’t provide enough detail to guide day-to-day decisions. Granular energy data—especially when broken down by system, time of day, and workload—enables smarter planning and continuous improvement. Examples include:
- Adjusting cooling dynamically based on actual IT load
- Identifying inefficiencies in specific server racks or cooling zones
- Verifying the impact of upgrades or layout changes
- Supporting ESG reporting and compliance with data-backed evidence
Platforms that bring together energy, temperature, and server performance data allow both facilities and IT teams to work from a shared view—and make more informed decisions.
Conclusion: Toward Resilient and Efficient Digital Infrastructure
Data centers will always be energy-intensive, but with the right tools and insights, they don’t have to be energy-wasteful. Incremental improvements—in visibility, cooling, airflow, and server utilization—can add up to meaningful reductions in cost and carbon impact.
In an increasingly digital world, energy-efficient data centers not only support business continuity—they also reflect responsible, future-focused operations.
References: